Faster: A Concurrent Key-Value Store with In-Place Updates
TL;DR
- 使用Epoch Protection Framework來避免lock operation
- 使用
in-placeupdate來避免I/O - 承上,設計hybrid Log Allocator混合
memory和diskaccess
Major components
Epoch Protection Framework
這套framework定義了三個變數:
- global shared atomic counter
- thread local counter
- which is strictly less all
每當thread做了某個operation,就會increase 並且把設定成,而且也可以在設定action,當的時候,就會執行這些action。
使用epoch的好處是保證了每個operation都是sequential,不會有並行處理的問題,而且只要某個timestamp is visble to all thread,就代表這個timestamp之前的操作都被所有thread acknowledge,保證了consistency。
Operations
- : 保留的entry給此thread,並且把更新到
- : 更新到, 到最大的"secure"值,並且把trigger 的所有action。
- : 把的值從變成,並且註冊到 。
- : 把thread 從中釋放。
Hash Index
Architecture
Index format
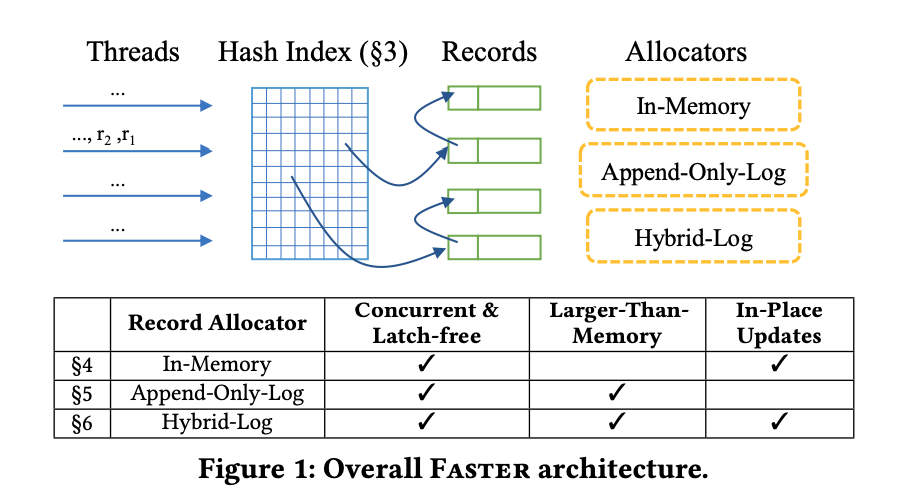
Hash index的數目為,每個hash index都是一個hash bucket,每個hash bucket的大小都跟cache line的大小一樣。要知道一個hash value分配到哪個hash bucket,只需要取vaule的後面個bits,就可以知道map到哪個hash bucket。
一個hash bucket會有n個8-byte的hash entry,hash entry設定為8-byte是因為在64-bit的系統可以做atomic的compare-and-swap。
Hash bucket和hash entry的format如下:
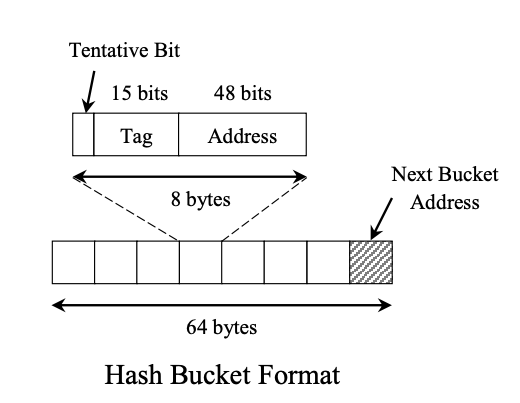
Hash entry
每個hash entry由三個部分組成:
- Tentative bit:用來表示此entry是否被使用
- Tag (up to 15 bits): Optional。但是可以跟offset來搭配組成,且此組合唯一。
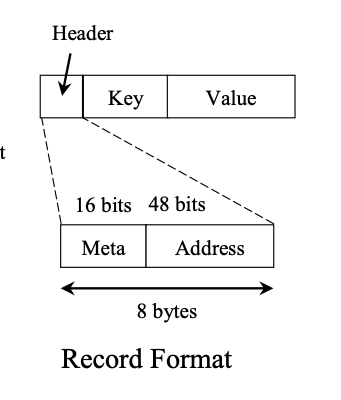
- Address (48 bits): 在
allocator裡面的位置。
Handle concurrent inserting same (offset, tag) pair
Index有三種operation:find, insert和delete,其中find和delete沒有concurrent的問題,所以只需要處理insert相同entry(相同的)的情況。
因為inserting的時候,是在hash bucket找第一個有empty的slot來insert,所以當兩個thread同時的insert了相同的,而在這時候又有另外一個thread刪除了bucket裡面的某個slot,那有可能導致兩個thread看到的第一個empty entry並不一樣,並且同時insert。
這邊採用的是2-phase的insertion。在做insertion的時候,thread會寫入entry並且set tentative bit,然後thread檢查是否有其他slot有相同的,如果有的話就reset tentative bit並且retry。
Hybrid Log Allocator
Head & Tail Offset
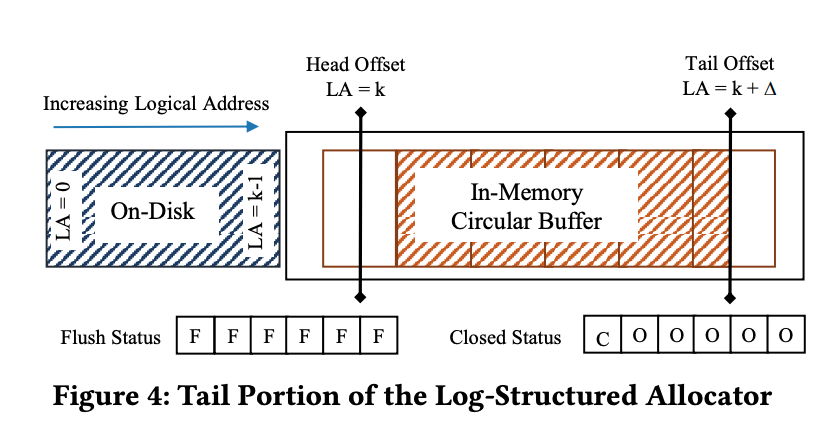
Head offset紀錄logical address space裡面,memory部分最低的可用位置。Tail offset指向memory部分下一個可用的位置。兩者的差代�表可用的記憶體大小,而差距的誤差時間約保持在一個固定時間(constant)。
Circular Buffer
Allocator額外用兩個array flush status和closed status來記錄哪些page被寫到second storage,哪些可以page可以被evict。
每當有新page被append,epoch就會bump,然後之前的page 就會被asynchonous的flush到second stroage。
而要evict page的時候,就增加head offset的值,然後bump epoch,並且在trigger action裡面set closed status。
In-place Update
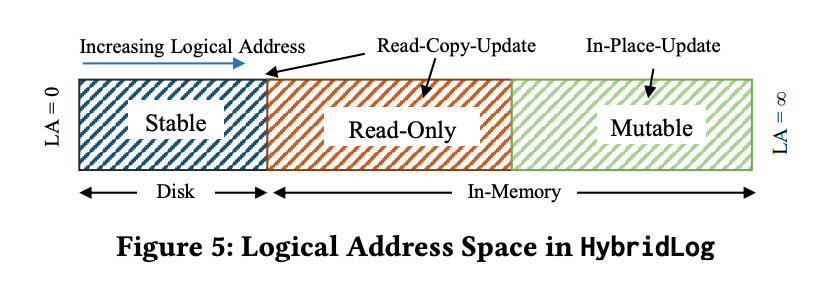
整個logical address space被分成三個部分:stable、read-only、mutable。
Stable: 在disk。無法in-place修改。
Read-only: 在memory。無法in-place修改,如果要修改會append一筆到mutable。概念上是準備被flush的page,但如果在flush之前被更新,就重新放回活躍區(mutable)。
Mutable: 在memory。如果修改會in-place的修改。
Fuzzy Region
以上的方法有個問題,如果mutable的區域因為某些thread的更新而變成read-only,但是這個變動還沒反應到所有thread,因此某些thread的data是stale。在這個情況,這些含有stale data的thread可能做in-place的update,導致inconsistent。
為了避免這個問題,需要額外一個新的marker: safe read-only offset。在read-only跟safe read-only之間的區域稱作fuzzy region,在不同的thread可能被視為read-only或mutable。
在fuzzy region的update有3種operation適用:
- Blind update: 這種操作適用在thread不考慮舊值的狀況,如果data stale,其他thread也會append一筆到
mutable,所以沒關係。 - Read-modify-write: 這種操作有可能會產生inconsistent,解決方法是把context記錄下來,defer到之後做。
- CRDT update: 如果data type是
CRDT,那可以各自做,之後在merge。
Recovery
HybridLog被當成WAL來使用,並且在flush的時候會紀錄tail offset的值,start和end的時候各有一個值。但因為有in-place update的關係,這兩個時間點之間的操作是fuzzy的,in-place update的行為可能發生在append前或後,所以無法判斷in-place的操作之中的order。
解決問題的方式被記錄在另外一篇paper。